How USB Connectors Enable Modern IoT, Industrial, Medical, and More
The USB connector, one of the most-used connection technologies for computer peripheral devices, can also make perfect sense for your product or system application. Employing a standardized interface, elegantly simple design, and robust materials, USB interconnects can save development budgets and design time in hundreds of uses. Shop Same Sky’s full range of USB connectors and USB cables.
USB Technology in Brief
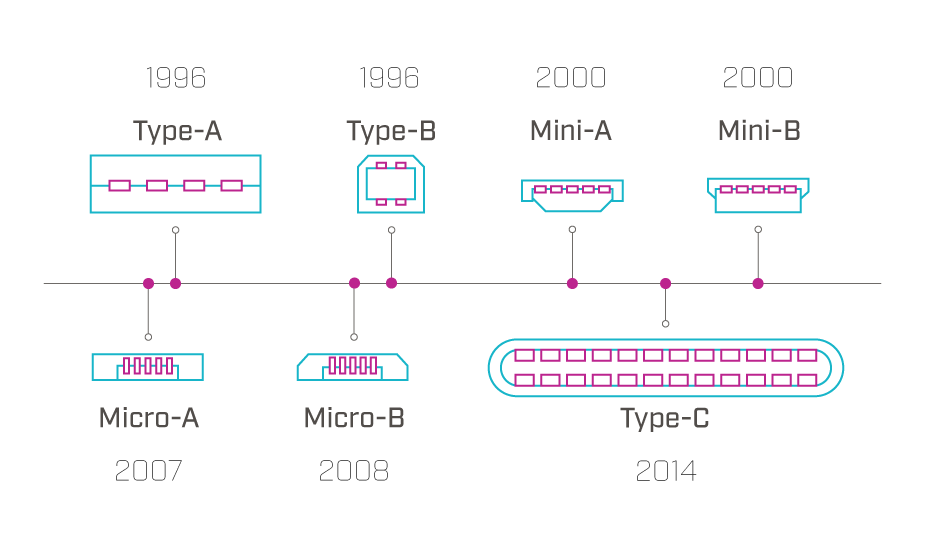
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is an interconnect solution born out of the computer connection chaos of the late 1990s. The technical protocols that underpin it have evolved over the years to add growing data processing speed and power handling capacity to each successive version of the standard and the hardware used with it.
The initial USB 1.1 version delivered data at 12 Mbps and power at 500 mA. The latest USB4 version transfers data at 80 Gbps and power at up to 240 W with USB PD 3.1. These improvements and others have widened the application range of USB technology from simple data transfer to heavy-duty use on the factory floor and beyond.
Interested in more USB connectors content? Check out our other blog topics:
- USB Connector Technology: A Deep Dive into Architecture, Pinouts, and Signaling
- Getting Started with USB: Integrating a USB Connector into Your Product
- What You Need to Know About USB Connectors and USB Cables
- USB Type C and USB 3.2 – Clarifying the Connection
- An Introduction to Power-Only USB Type C Connectors
- Or watch our USB connectors and standards video
USB-C Connectivity in IoT, Embedded, and Smart Devices
One of the newest applications for USB interconnect technology is the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT is popularly referred to as devices embedded with sensors and software allowing them to share information with each other via the internet.
IoT applications employ USB connectivity to shuttle data and power between IoT devices and a central gateway. This allows for easy charging, connected sensing capability, quick connection for IoT prototyping, testing and debugging, fast data flow for programming and software updates, and simple connection hardware options using USB-C or older connectors.
USB Type-C is a physical connector with a small, thin, and light form factor that is fully reversible, eliminating polarity errors or damage at insertion. It works with many versions of the USB standard to deliver high-speed data along with power up to 240 W via a single cable. This allows it to work with a broad range of devices for charging, data transfer, and video transmission.
USB-C is also used in embedded systems as a primary communication interface and ability to act as a host, device, or both depending on the application. Its small form factor along with efficient data and power delivery enables a single connection particularly suited to the needs of the small physical size of embedded systems. As with any new technology, there is a trade-off. While USB Type-C connectors are small and versatile for users, they introduce a level of complexity in their design, as they need to accommodate a wide range of power and broader communication standards. What used to be a simple connection between a cable and a port has now added a layer of embedded components.
Despite the additional challenge to developers, these USB-C features have still extended their use with many other technologies, including:
- Smart home devices: connecting sensors and actuators to a power hub for home monitoring and control.
- Robotics: communicating between robot hosts and peripherals on the factory floor.
- Handheld devices: providing a single cable, user-friendly connection for data and power.
- Medical devices: enabling simple and full-proof connections for data transfer from portable or stationary monitoring devices to a central host computer.
Existing designs using older USB interconnect technology can also be converted to USB-C. Depending on the version of the older USB connectors you are using, you will either need to use an adapter or add components, such as resistors, to ensure the devices can detect each other. You may also have to re-route some signals and ensure that the power delivery of the older system is adequate for your new needs. However, if you wish to take full advantage of all the benefits of a USB Type-C connector, the complexity level will increase as those embedded system layers discussed above come into play.
Advancements in USB Interconnect Standards
Applications for USB interconnection have also expanded due to ongoing improvements in the protocol. With the release of USB4 and related standards, additional features have been added to the technology. Here is a run-down of the most important ones:
- Enhanced security features: since its inception, the USB standard has not paid much attention to security. New features in the USB-C standard, however, have added cryptographic-based security authentication to allow devices to verify the legitimacy of connected devices and power sources prior to interaction. It also employs hardware-based encryption to protect data transfer along with a secure boot process to make sure only trusted software is loaded when a device is connected.
- Increased speeds: as we have noted, data transfer speeds have ramped up with the release of each new USB specification, beginning with USB 1.1 data transfer at 12 Mbps, and increasing to 80 Gbps with USB4 Version 2. These speeds have allowed for data-intense applications, like video.
- Expanded power delivery: power delivery levels have also steadily increased with each version of the USB standard up to the Extended Power Range (EPR) of 240 W (48 V, 5 A) with version 3.1. The USB Power Delivery (USB PD) standard was released in 2012. It not only increases power delivery over USB-C to 240 W, but also offers fixed voltages of 28 V, 36 V, and 48 V; provides adjustable intermediate voltages between 15 V and the maximum fixed voltage of the charger; allows bi-directional charging to both send and receive power; and features dynamic power flow, to adjust the power level to suit the needs of the connected device. USB-C can also support Gallium Nitride (GaN) charging technology used in fast chargers.

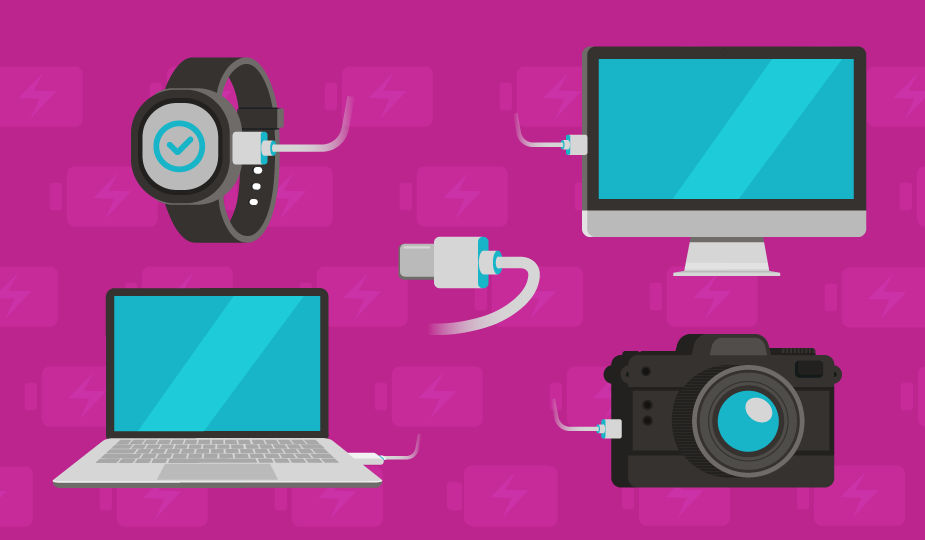
USB Connector Applications Across Key Industries
Some of the newer applications for the USB interconnect protocol and devices include consumer electronic products, industrial devices, and medical equipment. Here is a quick look at each.
USB Connectors in Consumer Electronics
Computers, video game consoles, and phones have long taken advantage of the benefits of USB technology to simplify connection. USB-C is also now used in a variety of adapters that allow you to listen to music or make calls while you are charging your phone and also supports volume control while fast charging your device. USB-C for phone charging also offers a smaller size connector than traditional jacks, reversibility for easy fault-free connection, and the ability to transmit digital audio for higher quality sound with headphones of earbuds. To keep costs down, Same Sky also offers power-only USB Type-C connectors, offering full interoperability with any USB-C cable while reducing pin count and complexity.
USB Connectors in Industrial Automation Systems
The process control systems used in factory automation employ USB interconnect technology to allow a wide variety of sensors, data loggers, vision system cameras, programmable logic controllers, human-machine interfaces, and other devices to communicate with a central control system. The data and power capacity of USB-C facilitates high-speed data exchange and power delivery via a single, standard connector instead of various serial or parallel ports. Being able to use a single connector also simplifies installation, replacement, and repairs or upgrades.
Industrial-grade USB connectors are also available using IP-rated seals, locking mechanisms, and rugged construction to withstand harsh vibration, moisture, temperature, and other factory floor conditions.
USB Connectors in Medical and Healthcare Devices
Patient monitors are rapidly evolving with improvements being driven by technological advances in digital miniaturization and remote systems. The increased adoption of personal health devices (PHDs), like wearable health trackers, home monitoring systems, and implantable devices has been supplemented by the convenience, simplicity, and performance of USB interconnect systems. With the widespread availability of USB ports on computers and smart phones, patients have a reliable, convenient, and familiar connection method to transfer data and files to their healthcare professionals.
Newer standards, like USB-C, offer the high-speed data transfer rates needed for complex patient data or image files along with power delivery for device charging. Medical grade USB connectors and cables are also available incorporating increased mating cycles and materials that resist humidity and moisture as well as offering ease of use in a homecare setting.
Summary
With up to 80 Gbps of data speed and 240 W of power delivery in the same connector, USB is an efficient, effective, and familiar interconnect technology for countless applications from basic data to video streaming and beyond.
The USB standard has been revised over the years to provide increasing data speeds and power. Newer versions that are yet to be introduced should keep it backwards compatible, increase current levels, enhance data speed, and reduce the physical size of the connector. In the meantime, the consideration of USB interconnect technology to streamline your device communication and connectivity remains an intelligent and efficient solution.
Key Takeaways
- USB interconnect technology supports data, power, and control in modern electronic systems, extending well beyond traditional computer peripherals.
- USB standards have significantly increased performance, scaling from 12 Mbps data transfer to up to 80 Gbps with USB4 and from 500 mA to 240 W with USB Power Delivery.
- USB-C enables data, power, and video over a single reversible connector, reducing connector count and simplifying system design.
- USB is widely used in IoT applications for device power, sensor data transfer, firmware updates, and rapid prototyping.
- Embedded systems leverage USB-C as a primary interface, supporting host, device, or dual-role operation depending on system needs.
- USB Power Delivery allows dynamic, bi-directional power negotiation, enabling fast charging and higher-power devices.
- Industrial and medical devices rely on USB for reliable, standardized connectivity, supporting high-speed data exchange and charging in demanding environments.
- USB remains a future-ready interconnect standard, maintaining backward compatibility while continuing to expand in speed, power, and functionality.