Memory Card Connectors: How SD, SIM, and Smart Cards Interface with Devices

Solid-state memory cards are used in many electronic devices and systems to expand usability, features, and convenience. As you might guess, most memory cards require compatible connector technology to enable them to mate with their host devices. The memory card connectors (or sockets) that are used must offer sustained hardware performance in systems that continue to miniaturize. But before we dive further into the connectors, let’s take a quick overview of memory card technology. Shop Same Sky’s full range of memory card connectors here.
What Are Memory Cards?
Memory cards are small, portable, solid-state devices that digitally store information like photos, videos, music, and all kinds of documents. They take advantage of flash memory technology, developed in the 1980’s, to store data even when the power is not on.
Flash memory is non-volatile data storage employing floating gate transistors, and due to the lack of moving parts, provides quick access times and proven reliability. This technology allows memory cards to be electronically erased and reprogrammed, making them ideal for secure data storage and quick retrieval.
Over the years since their introduction, memory cards have gone through many cycles of improvement that have centered on increased miniaturization of the cards and improved memory capacity. The versions available today include:
- SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) cards use a microchip to store information on a mobile device network plan along with user ID data. SIM cards are primarily used for network connectivity. Through the use of an international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number, they identify the subscriber and allow for the completion of calls, sending of texts, and access to data services on smartphones, tablets, and watches. SIM cards come in full-SIM (85.6 x 53.9 mm), mini-SIM (25 x 15 mm), micro-SIM (15 x 12 mm), and nano-SIM (12.3 x 8.8 mm) sizes. The original full-SIM was the size of a credit card and is no longer used. Because full-SIM is no longer used, mini-SIM—now commonly recognized by users as a full-size SIM card—is most often referred to simply as SIM or standard SIM. When it comes to mobile phone applications, mini-SIM and even micro-SIM have largely been replaced by nano-SIM. View Same Sky’s SIM card connectors offering.
- SD (Secure Digital) cards offer additional functionality to both store and transfer digital data. They can be used to store photos, music, videos, and other files and expand the digital storage capacity of the host device. They are commonly used in smartphones, digital cameras, tablet PCs, portable gaming consoles, and many other devices. SD cards have become the dominant memory card format in use today. Browse Same Sky’s SD card connectors product line.
- Smart Cards are credit card-size devices with an embedded computer chip that allows for additional functions, like identification, payment, and data encryption. Smart cards have additional features compared to other memory cards in that they can be wired, with physical connectors, or they can be contactless, or wireless. They do, however, require reader technology in the host device. Search Same Sky’s smart card connector models.

What Are SD Memory Cards?
The SD memory card technology standard was introduced by the SD Association in 1999 for information storage in portable devices. This standard has been developed over time to allow for more memory storage capacity and provide options for smaller packages. Today, they are available in three physical sizes: full or standardSD (32 x 24 mm); miniSD (21.5 x 20 mm); and microSD (15 x 11 mm), and in four memory storage capacity ranges:
- SDSC (Standard Capacity): up to 2 GB of storage
- SDHC (High Capacity): over 2 GB to 32 GB of storage
- SDXC (Extended Capacity): over 32 GB to 2 TB of storage
- SDUC (Ultra Capacity): over 2 TB to 128 TB of storage
SD memory cards also come in several data handling speeds to suit different applications ranging from basic data to high-speed video.
Memory Card Connector Insertion/Removal Methods
As we have mentioned, SIM and SD memory cards require a physical interconnect mechanism with the device they are supporting. This interconnect must offer smooth and reliable action for both insertion and ejection of the card. The connection mechanisms available today incorporate several different insertion and removal methodologies that include:
- Push-in/pull-out: the card is inserted into a slot in the device simply by pushing it in, requiring no further action to secure it. When removing, it is a simple pull-out motion, without any latching mechanism.
- Push-Push: the card is pushed into a slot to connect it and then pushed again to eject it using a spring mechanism, with audible click-in and click-out sounds (also known as Push-in/Auto Eject Out).
- Hinged: connector with a hinged locking mechanism that is used to lock down the card and ensure secure contact when exposed to vibration.
Memory Card Connector Contacts Explained
Both SD and SIM memory cards link with a device by way of designated circuit connection areas, or pins, on the card that allow for communication to a device through defined areas on the connector. Each pin completes a circuit with the connector and enables a specific function. The assignment of functions to the various pins is known as a contact or pinout.
The connection of a memory card to a device is accomplished through a separate connector, or socket, mounted on the host device. Card connectors are available in many different versions to match the card format needed for the device design.
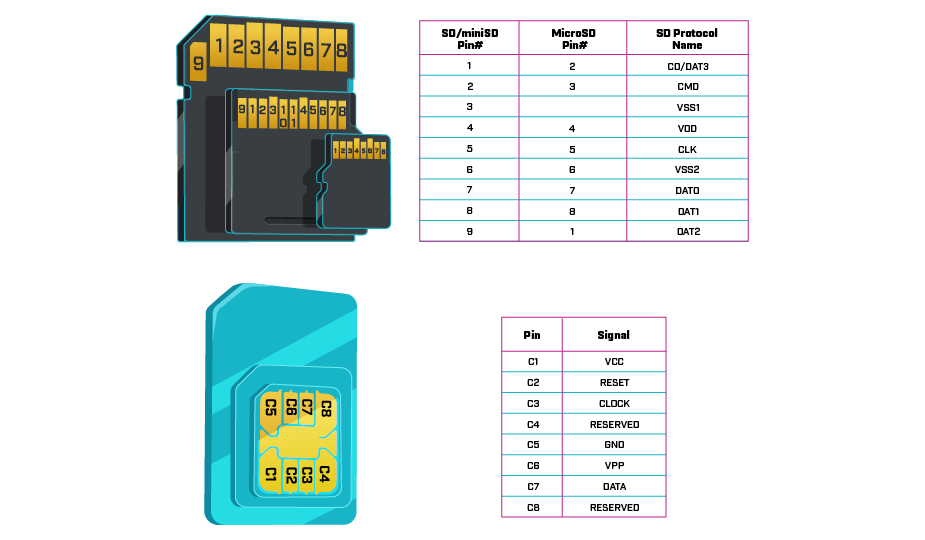
SD Card Connector Contacts
SD cards have evolved significantly over time, with multiple interface standards introduced to support increasing data transfer speeds. A standard full-size SD card typically has nine contact pins while microSD cards usually have eight pins. However, the exact pin count and configuration depends on the card type, with the highest speed classes requiring more pins. Modern SD cards support various communication protocols, including:
- SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface): These are commonly used in low-bandwidth applications, particularly in hobbyist projects due to their simplicity.
- SD (Secure Digital) Bus Interfaces: These include Default Speed, High Speed, UHS-I, UHS-II, and UHS-III standards. In some cases, these interfaces require additional rows of pins.
- PCIe/NVMe Interface: These are used with SD Express cards for ultra-high-speed applications.
SIM Card Connector Contacts
SIM cards contain from 6 to 8 pins, depending on the card size. On an 8-pin SIM card, the contact function assignments are:
- VCC: power supply
- GND: ground
- CLK: clock signal
- I/O: serial data input/output
- VPP: programming voltage
- RST: signal reset
- RFU: reserved for future use (typically assigned to 2 pins)
On a 6-pin SIM card, the pin assignments used are: VCC, GND, I/O, VPP, RST, and CLK. On some connectors, there is an additional pin or two for a card detect signal. This pin does not have an associated contact on the physical SIM card but is just a flexible conductor that gets connected to ground when a card is inserted in the socket.
Smart Card Connector Contacts
Smart cards, as we have noted, are credit card-size plastic cards with an embedded processor and various types of memory (RAM, EEPROM, and ROM). They interface with devices through physical contact via metal pads or contactless via radio frequency to communicate with a reader. Smart card connectors or sockets allow the cards to be easily inserted and read by a device and then removed. The contact function assignment names on smart cards are the same as those on 8-pin SIM cards.
What Are the Technical Standards for Memory Cards?
As with other electronic devices, the design landscape of memory cards continues to evolve to allow for enhanced features, faster data transfer, and smaller packages. Specifications for memory cards are typically covered in the ISO 7816 and ISO 7810 technical standards documents, which also define parameters for smart cards and their connectors. Updates to these specifications are released and implemented based on market demands, and manufacturers of cards and connectors are typically part of these developments.
What Is the Life Expectancy of Memory Card Connectors?
SIM and SD cards typically last from 5 to 10 years, depending on frequency of write and erase usage, insertion/removal, and environmental factors. As with other electromechanical devices, the durability of the connectors used with memory cards, including smart cards, hinges on their design, materials, and build quality. Typically, reputable brands offer connectors with more robust features. If your designs require a high frequency of usage, exposure to environmental conditions, protection from ESD, or locking or protection features, it makes sense to work closely with your supplier technical representative to ensure you get what you need.
What Are Common Memory Card Connector Applications?
The introduction of SIM memory cards allowed for efficient connectivity for mobile devices. The development of SD memory cards has greatly expanded the functionality of devices by allowing for secure and portable data transfer and memory storage. For a technology that began with mobile phones and other portable devices, the application landscape has broadened to include new and emerging solutions that include:
- Home security systems
- Gaming consoles and portable devices
- Virtual and augmented reality headsets
- Smart glasses
- The Internet of Things
- Drones
- Digital signage
- Wearable electronics
- Tablet computers
- GPS units
- Automotive data storage
Summary
Today’s memory card technologies enable high-performance products and services for a global audience that use electronic products to support and enhance their business, their life, and their enjoyment. There are many different physical connectors available today to support the variety of sizes and formats of both SD and SIM cards. These include connectors, ejectors, extenders, and adapters. Designed for manufacturability, SD, SIM, and smart card connectors can be either top or bottom-surface mounted and are available in ultra-compact profiles to support your design. Same Sky’s robust interconnection components for your memory card applications can add to your customer's user experience and enhance satisfaction with your products. As in many other areas, the demand for memory card solutions will continue to increase as emerging technologies are announced and advancements move into the marketplace.
Key Takeaways
- Memory card connectors enable communication between SIM, SD, and Smart Cards and their host devices.
- Common insertion/removal methods for memory card connectors include push-in/pull-out, push-push, and hinged mechanisms for secure card insertion and ejection.
- SD card connectors vary by card type and support multiple data protocols, including SPI, SD bus, and PCIe/NVMe.
- SIM and Smart Card connectors follow defined pinouts for power, data, and clock signals, with optional card detect features.
- Design considerations for memory card connectors include durability, insertion cycle rating, ESD protection, and compatibility with miniaturized devices.
- SD, SIM, and Smart Card connectors are available in compact, surface-mount formats for modern consumer and industrial electronics.
- Memory card connector applications range from smartphones and wearables to automotive systems, IoT devices, and digital signage.